Psychology of Design- Principles

First and foremost, We should have an understanding of what users want versus need before they ever encounter our designs. Therefore, psychological theories help to tackle effective designs. Every designer needs to learn about the fundamental of psychology. Because Psychology helps to create the design which will make users perform the actions they are expected.
What Is Psychology?
“Psychology” is a Greek word of the psyche. psychology, like much of science, is descriptive. However, psychologist define
“Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behaviour of humans”
Since Wilhelm Wundt opened the first psychology lab for the study of human behaviour in 1879 Leipzig, Germany, And psychologists study about various aspects of human behaviours such as personality, social culture, language, and brain functions.
There have described 6 main approaches in psychology. Psychodynamic, cognitive, humanistic, behaviourism, bio-psychological and social culture. Psychodynamic is the psychology that emphasizes the systematic study of the psychological forces that underlie human behaviour, feelings, and emotions.
Neuroscience combines biology and cognitive psychology. Cognitive psychology has at its heart process. how individuals will have with a given set of conditions: what small choices they will make; what they love, desire, become addicted to, see, smell, hear, touch, perceive and remember. Cognitive psychology like artificial intelligence.
Biology is a natural science that studies life and living organisms. Thus, neuroscience is a scientific approach to looking at psychology.
Humanistic emphasizes the study of the whole person, as a feeling, thinking, and the uniqueness of each individual. Humanistic psychologists look at human behaviour not only through the eyes of the observer, through the eyes of the person doing the behaving. Humanistic psychologists believe that an individual’s behaviour is connected to his inner feelings and self-image.
Behaviourism is behaviours that are acquired through conditioning. Behaviourism psychology can be objectively studied through observable actions.
Social culture describes an awareness of circumstances surrounding individuals and how their behaviours are affected specifically by their surrounding, social and cultural factors. Behaviour that relates to communication, sharing, co-operation, development, art and culture, societal pressures, norms and expected behaviours; in short, anything that describes humans in a social context.
Understanding Gestalt Principles
In 1910, These principles were found by Max Wertheimer and he had an insight when he observed a series of lights flashing on and off at a railroad crossing. And he and used by many product designers to create better interactions. This observation led to a set of descriptive principles about how was visually perceive objects. The gestalt principles show how the human eye preserves information and visual elements.
“The Whole is other than the sum of the Part”
— Kurt Koffka —
This quote the key idea behind the Gestalt Principle.
- Emergence- the process of forming a complex pattern for simple rules. The whole is identified before parts.
- Reification- Mind Fill in the gap
- Multi-Stability- Mind seeks to avoid uncertainty
- Invariance- Good to recognizing similarity and differences
This is the idea of playing the Gestalt Principles below. And also the main idea of the Gestalt Principles is about Perception and what is visually communicated by the object.

Law of Prägnanz
(good figure, Law of simplicity)
“People will perceive and interpret ambiguous or complex images as the simplest form(s) possible. because it is the interpretation that requires the least cognitive effort of us.”
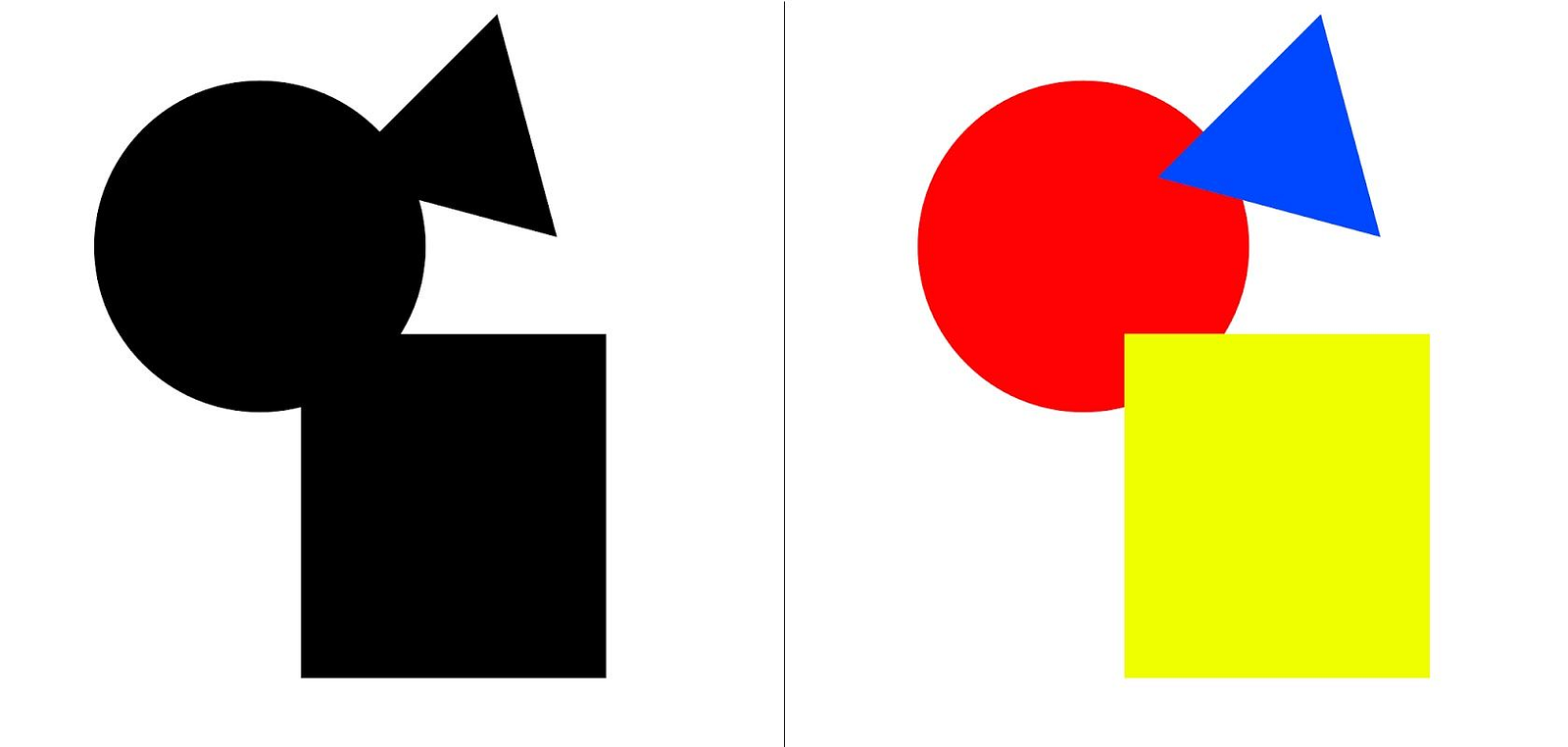
Closure
“When seeing a complex arrangement of elements, we tend to look for a single, recognizable pattern.”
Closer is the opposite of what we see in the Prägnanz image. As humans, we are a curious bit of creatures. Human eyes are made to see complete shapes. When they are not complete the possibility of humans thinking that there is more of the shape in the hidden space is greater than seeing the full object. When a human sees the full object, they observe and conclude that that point to be the stopping point. The best thing is to keep the continuity of the application.
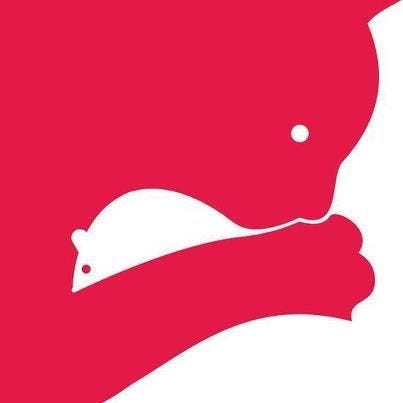

In this above image, you should see a red background even though the image is actually comprised of rabbit shapes. On the image, you see a rat even though the figure is several random shapes in white background.
Proximity
“Objects that are closer together are perceived as more related than objects that are further apart.”
When objects are placed in close proximity, they tend to shape a single group. Normally the human brain creates relationships between similar elements that are close together. If you take an example,(figure 3) when elements are close together we think it’s one group, and when they are distance we think that they are individual objects but not as a group.
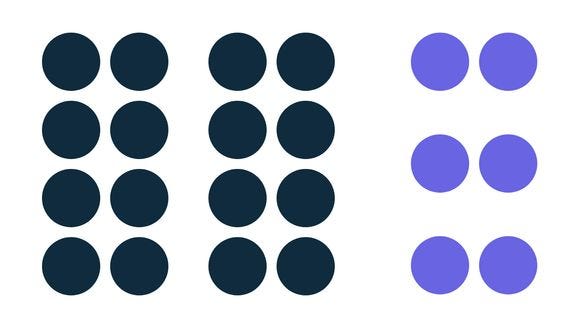
In the above image, you can see the shape, colour, and space between the object and you can group one another.
Figure/Ground
“Elements are perceived as either figure (the element in focus) or ground (the background on which the figure rests).”
Our eyes are made in a way to understand and differentiate elements from its background. If the elements are not distinguishable from the background the elements blends with the background the user might miss important messages and details. That creates frustration in users.

In the above image, you either see a butterfly or two men depending on whether you see the white color as a figure and the white as ground or butterfly.
In design, Gestalt principles play a major role in the part of psychology. It will support the designers to create a product that solves a particular problem by understanding and predicting user behavior.
Fitts’s Law
The time to acquire a target is a function of the distance to and size of the target
To understand more about the psychology and design the next principle that I have looked into it is the Fitts law. It’s a very simple principle as well. When this principle explains object size and functions. When objects are bigger with their functions which are built-in, it’s very easy for the user to understand and interact with the object. Furthermore, when the objects with functions are placed close to human reach it is really easy for the user to interact with it.
Fitts’s Law faster to hit a larger target close to you, than a small target further from you. Now you are thinking that it should be easy enough to go off and find another equally apparent statement and make a law about it. The think is Fitts didn’t just make the law. He backed up with science, making an equation.
MT = a + b log2 (A / W + 1)
MT =dependent variable
a and b =regression coefficients
A =distance or amplitude to move,W =width of the region within which the move terminates.
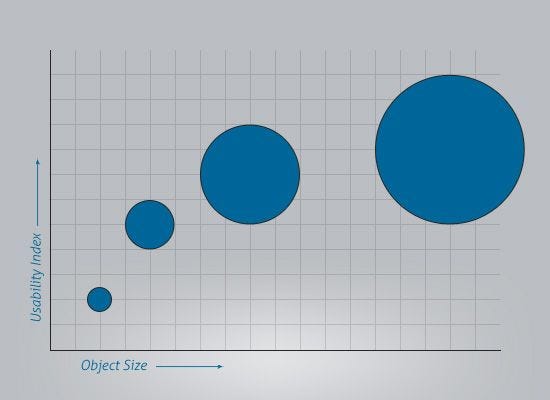
The chart on top illustrates the target size increases the usability of the application also increases. In an application, when the distance increases between the action it takes a longer time to access the function, and when the object increases in size it becomes difficult to access the object. When humans interact with the applications the time humans spend on the application creates emotions towards the users. When the time increases to complete a task, the user feels frustrated and given up completing the task.
As an example, The brake pedal in the car is bigger than the accelerator pedal. It’s also closer to you and that makes it faster and easier to hit in an emergency.
And another example is, the button for switching on heavy machinery is small and recessed; the button for stopping. It is large and prominent. You don’t want people to start machines by accident, but you do want them to be very easy to stop if there is a problem.
Comments
Post a Comment